Book Banning One: Difference between revisions
AnnabelleP (talk | contribs) |
Meacellitto (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Book banning- in its simplest terms- is the process of removing access to a book from certain book-providing places, most commonly school and public libraries. | Book banning- in its simplest terms- is the process of removing access to a book from certain book-providing places, most commonly school and public libraries. | ||
Book banning typically occurs in three stages. The first stage being when a certain topic is censored. Throughout history, commonly censored themes have been issues of race, sex, gender and sexual identity, and violence. Sexual content is the most likely reason a book is to be banned, due to the topic being heavily censored in public and school libraries. | Book banning typically occurs in three stages. The first stage being when a certain topic is censored. Throughout history, commonly censored themes have been issues of race, sex, gender and sexual identity, and violence.<ref name=":0">Brady, Amy. “The History (and Present) of Banning Books in America.” ''Literary Hub'', 22 Sept. 2016, lithub.com/the-history-and-present-of-banning-books-in-america/.</ref> Sexual content is the most likely reason a book is to be banned, due to the topic being heavily censored in public and school libraries.<ref name=":1">Staff. “DeSantis Signs Bill on School Books, Term Limits.” ''Tallahassee Reports'', 26 Mar. 2022, tallahasseereports.com/2022/03/26/desantis-signs-bill-on-school-books-term-limits/. Accessed 21 Oct. 2025.</ref> | ||
The second stage of book banning is when a book is challenged. Concerned community members- often parents, administrators, or organizations- petition their local library or their children's library to have a title removed, often being because it contains commonly censored material. Very rarely is a challenge carried out by librarians or educators. | The second stage of book banning is when a book is challenged. Concerned community members- often parents, administrators, or organizations- petition their local library or their children's library to have a title removed, often being because it contains commonly censored material.<ref name=":2">Bristow, Holly. “Moms 4 Liberty Brevard Asking for 19 More Books to Be Pulled from School Libraries.” ''FOX 35 Orlando'', 23 Mar. 2022, www.fox35orlando.com/news/moms-4-liberty-brevard-asking-for-19-more-books-to-be-pulled-from-school-libraries.</ref> Very rarely is a challenge carried out by librarians or educators. | ||
The final stage is the result of a successful book challenge campaign: a book ban. A title can be banned by authority figures over the library, commonly seen as school administrators but governments have been involved to orchestrate state-wide bans of books. | The final stage is the result of a successful book challenge campaign: a book ban. A title can be banned by authority figures over the library, commonly seen as school administrators but governments have been involved to orchestrate state-wide bans of books.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
=== Effect on Authors and Publishers === | === Effect on Authors and Publishers === | ||
'''Effect on Authors''' | |||
One of the main ways book banning takes a toll on authors is they receive many fewer, if any, invitations to visit schools. These visits would typically entail the author sharing their book and its message with young people, but the more books continue to be banned, the fewer authors are permitted to have their books on the shelves of these libraries, much less be invited to speak there. In addition to this being a great detriment to the students and the media they are able to consume, this hurts the author because school visitations often account for a significant amount of their salary, and without that, their ability to sustain their lifestyle as an author could be put at stake.<ref name=":3">“The Normalization of Book Banning.” ''PEN America'', 1 Oct. 2025, <nowiki>https://pen.org/report/the-normalization-of-book-banning/</nowiki>.</ref> They also face increased social media scrutiny and harassment as an author of a banned book, and may be dissuaded from writing about similar topics in the future.<ref name=":3" /> | |||
'''Effect on Publishers''' | |||
Some publishers such as Macmillan and Penguin Random House are fighting book bans and trying to preserve books on a wide variety of subjects, even the ones being banned. However, other publishers may be more cautious about accepting books that fit into "risky" themes such as previously stated. <ref name=":4">''Book Bans Are ‘Common and Rampant.’ So Are Educators and Parents Fighting Them. | NEA''. <nowiki>https://www.nea.org/nea-today/all-news-articles/book-bans-are-common-and-rampant-so-are-educators-and-parents-fighting-them</nowiki>. Accessed 9 Nov. 2025.</ref>Similarly, the restriction of media in the U.S and other nations prevents certain books being published in other countries because that country may not allow the content to be shared. | |||
=== A Brief History === | === A Brief History === | ||
The first records of book banning occurred in B.C. China, with an emperor destroying anti-dynasty propaganda. However in America, the first major instance of book banning occurred with Uncle Tom's Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1852. This book was widely banned in southern states for being anti-slavery during a time in which America's tensions over racial disparity were coming to a boil that would eventually result in the Civil War. | The first records of book banning occurred in B.C. China, with an emperor destroying anti-dynasty propaganda. However in America, the first major instance of book banning occurred with Uncle Tom's Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1852.<ref name=":0" /> This book was widely banned in southern states for being anti-slavery during a time in which America's tensions over racial disparity were coming to a boil that would eventually result in the Civil War. | ||
Another famous instance of book banning in America came from the Comstock laws. A pious man named Anthony Comstock proposed in 1873 that a law be put in place that would disallow pornographic material to be sent by mail. This ranged from anything by Oscar Wilde to anatomy textbooks. These laws were finally lifted by a judge in the 1920s when Ulysses was challenged for pornographic content. | Another famous instance of book banning in America came from the Comstock laws. A pious man named Anthony Comstock proposed in 1873 that a law be put in place that would disallow pornographic material to be sent by mail.<ref name=":0" /> This ranged from anything by Oscar Wilde to anatomy textbooks. These laws were finally lifted by a judge in the 1920s when Ulysses was challenged for pornographic content.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
One of the most famous and more recent examples of book banning were the book burnings that occurred during World War 2. The most prominent one took place on May 10th in 1933, but burning books written by Jewish authors and containing censored material was common practice in Germany throughout that period. | One of the most famous and more recent examples of book banning were the book burnings that occurred during World War 2. The most prominent one took place on May 10th in 1933, but burning books written by Jewish authors and containing censored material was common practice in Germany throughout that period.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
Book banning has always been a practice in censorship, and certain themes have always been restricted in access. Book banning today looks a lot more politicized, and while there is less physical burning, there are many more people outraged at what is banned versus isn't. Liberals tend to lean more in favor of not banning books while conservatives offer the counterpoint of not wanting to expose children to possibly harmful content. America's struggle to walk this thin line has made headlines, upsetting both sides of the issue for years. | Book banning has always been a practice in censorship, and certain themes have always been restricted in access.<ref name=":0" /> Book banning today looks a lot more politicized, and while there is less physical burning, there are many more people outraged at what is banned versus isn't. Liberals tend to lean more in favor of not banning books while conservatives offer the counterpoint of not wanting to expose children to possibly harmful content.<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /> America's struggle to walk this thin line has made headlines, upsetting both sides of the issue for years. | ||
== Reasons Books Become Banned == | |||
For years books have been getting censored or banned. Bans typically occur because there is some type of content within a book deeming it as "obscene". What defines a books as obscene has changed over the years, but some of the things that have stayed consistent are profane language, LGBTQ+ content and communities<ref name=":4" />, descriptions of rape and sexual assault, and anything with sexual content. Overall the fear in books has become prominent when focused on content being "age-appropriate". | |||
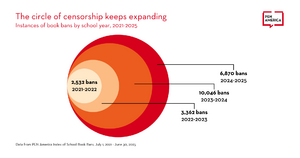
= | Though the reasons for banning have remained relatively consistent throughout the years, recently it's believed to have become "systematic", seen to have become normalized.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
[[File:The-circle-of-censorship-keeps-expanding-1920x1008.png|thumb|Book bans have been increasing over the years]][[File:Banned Books 2025small.jpg|thumb|This showcases the 10 most challenged books of 2024]] | |||
== | == Reasons For and Against Banning == | ||
=== For Book Banning === | |||
'''Who bans books?''' | |||
* School Boards and administrators | |||
* Both state and national level politicians | |||
'''Their reasoning''' | |||
* They believe parents have a right to control what their children read | |||
* Also they say they need to protect children from "immature content" in whatever forms that may take. However the word immature or obscene has many complex definitions | |||
* They want to restrict access to sexually explicit content, which has been interpreted to include anything LGBTQ+ related <ref name=":4" /> | |||
=== Against Book Banning === | |||
'''Who disagrees with banning books?''' | |||
* National Coalition Against Censorships | |||
* Many libraries, such as the American Library Association | |||
* Often authors and publishers | |||
'''Their reasoning''' | |||
* Censoring books forces students to lose access to important information of messages that books can spread | |||
* Students will be unable to identify with books that censor parts of their identity | |||
* Banning books erases the real, lived experiences of those who went through violence or harassment and want to share their voice<ref name=":4" /> | |||
== Solutions == | == Solutions == | ||
* | * The best way to fight book banning is to actively use your voice. Supporting authors, attending school board meetings, and voting are all great ways to impact and influence the people making the decisions.<ref>“5 Ways to Fight Book Bans.” ''PEN America'', <nowiki>https://pen.org/book-bans/5-ways-to-fight-book-bans/</nowiki>. Accessed 7 November 2025.</ref> Using your voice and vote can have a big impact. | ||
== Notes == | |||
[[ Category:Publishing Problems ]] | [[ Category:Publishing Problems ]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:11, 9 November 2025

What is Book Banning?
Book banning- in its simplest terms- is the process of removing access to a book from certain book-providing places, most commonly school and public libraries.
Book banning typically occurs in three stages. The first stage being when a certain topic is censored. Throughout history, commonly censored themes have been issues of race, sex, gender and sexual identity, and violence.[1] Sexual content is the most likely reason a book is to be banned, due to the topic being heavily censored in public and school libraries.[2]
The second stage of book banning is when a book is challenged. Concerned community members- often parents, administrators, or organizations- petition their local library or their children's library to have a title removed, often being because it contains commonly censored material.[3] Very rarely is a challenge carried out by librarians or educators.
The final stage is the result of a successful book challenge campaign: a book ban. A title can be banned by authority figures over the library, commonly seen as school administrators but governments have been involved to orchestrate state-wide bans of books.[2]
Effect on Authors and Publishers
Effect on Authors
One of the main ways book banning takes a toll on authors is they receive many fewer, if any, invitations to visit schools. These visits would typically entail the author sharing their book and its message with young people, but the more books continue to be banned, the fewer authors are permitted to have their books on the shelves of these libraries, much less be invited to speak there. In addition to this being a great detriment to the students and the media they are able to consume, this hurts the author because school visitations often account for a significant amount of their salary, and without that, their ability to sustain their lifestyle as an author could be put at stake.[4] They also face increased social media scrutiny and harassment as an author of a banned book, and may be dissuaded from writing about similar topics in the future.[4]
Effect on Publishers
Some publishers such as Macmillan and Penguin Random House are fighting book bans and trying to preserve books on a wide variety of subjects, even the ones being banned. However, other publishers may be more cautious about accepting books that fit into "risky" themes such as previously stated. [5]Similarly, the restriction of media in the U.S and other nations prevents certain books being published in other countries because that country may not allow the content to be shared.
A Brief History
The first records of book banning occurred in B.C. China, with an emperor destroying anti-dynasty propaganda. However in America, the first major instance of book banning occurred with Uncle Tom's Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1852.[1] This book was widely banned in southern states for being anti-slavery during a time in which America's tensions over racial disparity were coming to a boil that would eventually result in the Civil War.
Another famous instance of book banning in America came from the Comstock laws. A pious man named Anthony Comstock proposed in 1873 that a law be put in place that would disallow pornographic material to be sent by mail.[1] This ranged from anything by Oscar Wilde to anatomy textbooks. These laws were finally lifted by a judge in the 1920s when Ulysses was challenged for pornographic content.[1]
One of the most famous and more recent examples of book banning were the book burnings that occurred during World War 2. The most prominent one took place on May 10th in 1933, but burning books written by Jewish authors and containing censored material was common practice in Germany throughout that period.[1]
Book banning has always been a practice in censorship, and certain themes have always been restricted in access.[1] Book banning today looks a lot more politicized, and while there is less physical burning, there are many more people outraged at what is banned versus isn't. Liberals tend to lean more in favor of not banning books while conservatives offer the counterpoint of not wanting to expose children to possibly harmful content.[2][3] America's struggle to walk this thin line has made headlines, upsetting both sides of the issue for years.
Reasons Books Become Banned
For years books have been getting censored or banned. Bans typically occur because there is some type of content within a book deeming it as "obscene". What defines a books as obscene has changed over the years, but some of the things that have stayed consistent are profane language, LGBTQ+ content and communities[5], descriptions of rape and sexual assault, and anything with sexual content. Overall the fear in books has become prominent when focused on content being "age-appropriate".
Though the reasons for banning have remained relatively consistent throughout the years, recently it's believed to have become "systematic", seen to have become normalized.[4]

Reasons For and Against Banning
For Book Banning
Who bans books?
- School Boards and administrators
- Both state and national level politicians
Their reasoning
- They believe parents have a right to control what their children read
- Also they say they need to protect children from "immature content" in whatever forms that may take. However the word immature or obscene has many complex definitions
- They want to restrict access to sexually explicit content, which has been interpreted to include anything LGBTQ+ related [5]
Against Book Banning
Who disagrees with banning books?
- National Coalition Against Censorships
- Many libraries, such as the American Library Association
- Often authors and publishers
Their reasoning
- Censoring books forces students to lose access to important information of messages that books can spread
- Students will be unable to identify with books that censor parts of their identity
- Banning books erases the real, lived experiences of those who went through violence or harassment and want to share their voice[5]
Solutions
- The best way to fight book banning is to actively use your voice. Supporting authors, attending school board meetings, and voting are all great ways to impact and influence the people making the decisions.[6] Using your voice and vote can have a big impact.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Brady, Amy. “The History (and Present) of Banning Books in America.” Literary Hub, 22 Sept. 2016, lithub.com/the-history-and-present-of-banning-books-in-america/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Staff. “DeSantis Signs Bill on School Books, Term Limits.” Tallahassee Reports, 26 Mar. 2022, tallahasseereports.com/2022/03/26/desantis-signs-bill-on-school-books-term-limits/. Accessed 21 Oct. 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bristow, Holly. “Moms 4 Liberty Brevard Asking for 19 More Books to Be Pulled from School Libraries.” FOX 35 Orlando, 23 Mar. 2022, www.fox35orlando.com/news/moms-4-liberty-brevard-asking-for-19-more-books-to-be-pulled-from-school-libraries.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 “The Normalization of Book Banning.” PEN America, 1 Oct. 2025, https://pen.org/report/the-normalization-of-book-banning/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Book Bans Are ‘Common and Rampant.’ So Are Educators and Parents Fighting Them. | NEA. https://www.nea.org/nea-today/all-news-articles/book-bans-are-common-and-rampant-so-are-educators-and-parents-fighting-them. Accessed 9 Nov. 2025.
- ↑ “5 Ways to Fight Book Bans.” PEN America, https://pen.org/book-bans/5-ways-to-fight-book-bans/. Accessed 7 November 2025.
